Learn about atomic
absorption spectroscopy in 5 minutes. This article
discusses the AAS (atomic absorption spectroscopy) principle and Instrumentation
of AAS. This article will help students comprehend AAS (atomic
absorption spectroscopy) on their exam.
Spectroscopy
Spectroscopy, study of the absorption and emission of light and other radiation by matter, as related to the dependence of these processes on the wavelength of the radiation.
Absorption spectroscopy
If electromagnetic radiation of a certain range of wavelengths passes
through the analyzed substance, the radiation of certain wavelengths is
absorbed by the substance. The study of this is called absorption spectroscopy.
The absorbed wavelength characterizes a certain specific functional group of
the compound or the compound itself.
Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy
- This method includes the study of absorption and radiation by neutral atoms in the vaporous state.
- In AAS, when a solution containing a mixture of metallic species is introduced into a flame, the solvent is evaporated and vapors of the metallic species are obtained, and then the absorption of radiation by the atomic pairs is measured at a selected characteristic wavelength each individual.
- This technique is also called absorption flame photometry because all applications of analyte atomic absorption involve spraying a sample solution into a flame.
- It can analyze over 62 elements.
- It also determines the metal concentration in the sample.
- In this periodic table, elements observable via atomic absorption are shown in pink.
Instrumentation of atomic absorption spectroscopy
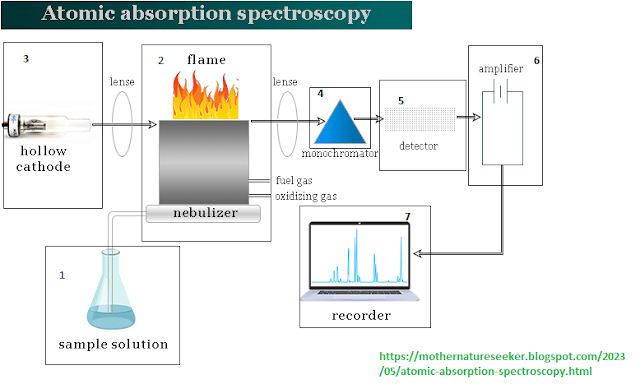 |
Instrumentation of atomic
absorption spectroscopy |
For instrumentation,
flame, flameless, and graphite furnaces are available in atomic absorption
apparatus. Any atomic absorption spectroscopy device has the following types of
components:
- Nebulizer
- Atomizer
- Light source (Hollow cathode lamp)
- Monochromator
- Detector
- Recorder
Nebulizer
- Aspirate liquid samples at a controlled rate.
- Create a fine aerosol spray to introduce into the flame.
- Thoroughly mix the aerosol, fuel and oxidizer for introduction into the flame.
Atomizer
- The elements to be analysed must be in the atomic state.
- Atomization is the division of particles into individual molecules and the breaking of molecules into atoms.
- This is accomplished by treating the analyte to high temperatures in a flame or graphite furnace.
 |
| Types of atomizers |
Flame atomizer
- Oxidant gas and fuel gas must be mixed together to create a flame.
- Air-acetylene or nitrous oxide-acetylene flames are often used.
- Liquid or solution samples are usually used in flame atomizers.
Graphite tube atomizer
- The sample is vaporized using a furnace coated with graphite.
- In GFAAS, the samples are stored in a small tube coated with graphite, which can then be heated to vaporize and atomize the analyte.
- The graphite tubes are heated using a high voltage source.
Light source
- Hollow cathode lamps are the most common source of radiation in AAS.
- A hollow cathode discharge lamp with a tungsten anode and a cylindrical analytical metal cathode in a glass tube with a filling gas such as Ne (neon) or Ar (argon).
- Each element has its own unique lamp that must be used for this analysis.
Monochromator
- This is a very important part of the AA spectrometer. It is used to separate all thousands of rows.
- A monochromator is used to select the wavelength of light that is absorbed by the sample while excluding other wavelengths.
- The selection of a specific light allows the determination of the selected element in the presence of others.
Detector
- The detector can change the monochromator's light into an improved on simplified electrical signal.
- In general, we used a photomultiplier as a detector in an atomic absorption spectroscopy instrument. The detector can be tuned to respond to a specific wavelength or frequency.
- Electrical signal processing is provided by a signal amplifier. The signal can be displayed for reading or further fed to the data station for printing in the required format.
Recorder
- The recorder can receive electrical signals from the detector and convert them into a readable response.
- Today, in the
instrumentation of atomic absorption spectroscopy, we used a computer system
with appropriate software to recode the signals coming from the detector.
Calibration Curve
- A calibration curve is used for estimating an element's unknown concentration in a solution. The device is calibrated using several solutions of known concentrations.
- The absorbance of each known solution is measured and then a concentration vs. absorbance curve is plotted.







0 Comentaris